You should not try it!
Applying Private Investment Analysis to the Rash of Mega-IPOs Occurring
The first half of 2019 saw a steady stream of technology IPOs. First Lyft, then Uber, then Zoom, all with different business models and revenue structures. As an early investor in technology companies, I spend a lot of time evaluating models for Venture Capital, but as a (recovering) investment analyst, I also like to take a view around how to structure a probability weighted investment once these companies have hit the public markets. The following post outlines a recent approach that I took to manage the volatility and return in these growth stocks.
Question: Which of the Recent technology IPOs Stands out as a Winning Business Model?
Investing in Lyft and Uber, post IPO, had little interest for me. On the positive side, Lyft revenue growth was 95% in Q1, 2019, but it had a negative contribution margin in 2018 and Q1 2019. Uber’s growth was a much lower 20% in Q1, but it appears to have slightly better contribution margin than Lyft, possibly even as high as 5%. I expect Uber and Lyft to improve their contribution margin, but it is difficult to see either of them delivering a reasonable level of profitability in the near term as scaling revenue does not help profitability until contribution margin improves. Zoom Video, on the other hand, had contribution margin of roughly 25% coupled with over 100% revenue growth. It also seems on the verge of moving to profitability, especially if the company is willing to lower its growth target a bit.
Zoom has a Strong Combination of Winning Attributes
There is certainly risk in Zoom but based on the momentum we’re seeing in its usage (including an increasing number of startups who use Zoom for video pitches to Azure), the company looks to be in the midst of a multi-year escalation of revenue. Users have said that it is the easiest product to work with and I believe the quality of its video is best in class. The reasons for Zoom’s high growth include:
- Revenue retention of a cohort is currently 140% – meaning that the same set of customers (including those who churn) spend 40% more a year later. While this growth is probably not sustainable over the long term, its subscription model, based on plans that increase with usage, could keep the retention at over 100% for several years.
- It is very efficient in acquiring customers – with a payback period of 7 months, which is highly unusual for a SaaS software company. This is partly because of the viral nature of the product – the host of the Zoom call invites various people to participate (who may not be previous Zoom users). When you participate, you download Zoom software and are now in their network at no cost to Zoom. They then offer you a free service while attempting to upgrade you to paid.
- Gross Margins (GMs) are Software GMs – about 82% and increasing, making the long-term model likely to be quite profitable
- Currently the product has the reputation of being best in class (see here) for a comparison to Webex.
- Zoom’s compression technology is well ahead of any competitor according to my friend Mark Leslie (a superb technologist and former CEO of Veritas).
The Fly in the Ointment: My Valuation Technique shows it to be Over Valued
My valuation technique, published in one of our blog posts, provides a method of valuing companies based on revenue growth and gross margin. It helps parse which sub-scale companies are likely to be good investments before they reach the revenue levels needed to achieve long term profitability. For Zoom Video, the method shows that it is currently ahead of itself on valuation, but if it grows close to 100% (in the January quarter it was up 108%) this year it will catch up to the valuation suggested by my method. What this means is that the revenue multiple of the company is likely to compress over time.
Forward Pricing: Constructing a Way of Winning Big on Appreciation of Even 10%
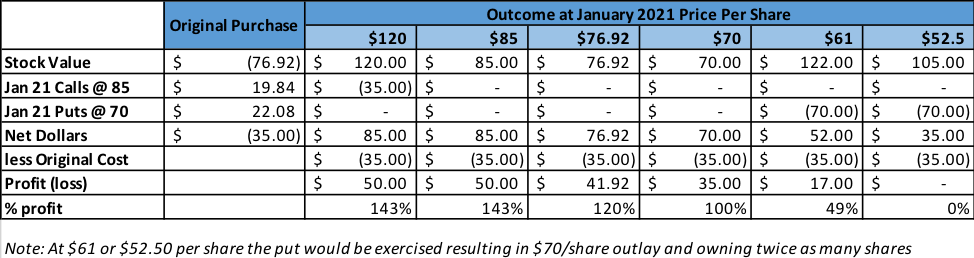
So instead of just buying the stock, I constructed a complex transaction on May 29. Using it, I only required the stock to appreciate 10% in 20 months for me to earn 140% on my investment. I essentially “pre-bought” the stock for January 2021 (or will have the stock called at a large profit). Here is what I did:
- Bought shares of stock at $76.92
- Sold the same number of shares of call options at $85 strike price for $19.84/share
- Sold the same number of shares of put options at $70 strike for $22.08/share
- Both sets of options expire in Jan 2021 (20 months)
- Net out of pocket was $35/share
Given the momentum I think there is a high probability (75% or so) that the revenue run rate in January 2021 (when options mature) will be over 2.5x where it was in Q1 2019. If that is the case, it seems unlikely that the stock would be at a lower price per share than the day I made the purchase despite a potential for substantial contraction of Price/Revenue.
In January 2021, when the options expire, I will either own the same shares, or double the number of shares or I will have had my shares “called” at $85/share.
The possibilities are:
- If the stock is $85 or more at the call date, the stock would be called, and my profit would be roughly 140% of the net $35 invested
- If the stock is between $70 and $85, I would net $42 from the options expiring worthless plus or minus the change in value from my purchase price of $76.92. The gain would exceed 100%
- If the stock is below $70, I’ll own 2x shares at an average price of $52.50/share – which should be a reasonably good price to be at 20 months out.
- Of course, the options can be repurchased, and new options sold during the time period resulting in different outcomes.
Break-Even Point for the Transaction Is a 32% Decline in Zoom Video Stock Price
Portfolio Managers that are “Value Oriented” will undoubtedly have a problem with this, but I view this transaction as the equivalent of a value stock purchase (of a high flyer) since the break-even of $52/share should be a great buy in January 2021. Part of my reasoning is the downside protection offered: where my being forced to honor the put option would mean that in January 2021, I would own twice the number of shares at an average price of $52.50/share. If I’m right about the likelihood of 150% revenue growth during the period, it would mean price/revenue had declined about 73% or more. Is there some flaw in my logic or are the premiums on the options so high that the risk reward appears to favor this transaction?
I started writing this before Zoom reported their April quarter earnings, which again showed over 100% revenue growth year/year. As a result, the stock jumped and was about $100/share. I decided to do a similar transaction where my upside is 130% of net dollars invested…but that’s a story for another day.
Estimating the “Probabilistic” Return Using My Performance Estimates
Because I was uncomfortable with the valuation, I created the transaction described above. I believe going almost 2 years out provides protection against volatility and lowers risk. This can apply to other companies that are expected to grow at a high rate. As to my guess at probabilities:
- 75% that revenue run rate is 2.5x January 2019 (base) quarter in the quarter ending in January 2021. A 60% compound annual growth (CAG) for 2 years puts the revenue higher (they grew over 100% in the January 2019 quarter to revenue of $105.8M)
- 95% that revenue run rate is over 2.0X the base 2 years later (options expire in January of that year). This requires revenue CAG of 42%. Given that the existing customer revenue retention rate averaged 140% last year, this appears highly likely.
- 99% that revenue is over 1.5X the base in the January 2021 quarter (requires slightly over 22% CAG)
- 1% that revenue is less than 1.5X
Assuming the above is true, I believe that when I did the initial transaction the probabilities for the stock were (they are better today due to a strong April quarter):
- 50% that the stock trades over 1.5X today by January 2021 (it is almost there today, but could hit a speed bump)
- 80% that the stock is over $85/share (up 10% from when I did the trade) in January 2021
- 10% that the stock is between $70 and $85/share in January 2021
- 5% that the stock is between $52 and $70 in January 2021
- 5% that the stock is below $52
Obviously, probabilities are guesses since they heavily depend on market sentiment, whereas my revenue estimates are more solid as they are based upon analysis, I’m more comfortable with. Putting the guesses on probability together this meant:
- 80% probability of 140% profit = 2.4X
- 10% probability of 100% profit = 2.0X
- 5% probability of 50% profit (this assumes the stock is in the middle at $61/share) = 1.5X
- 5% probability of a loss assuming I don’t roll the options and don’t buy them back early. At $35/share, loss would be 100% = (1.0X)
If I’m right on these estimates, then the weighted probability is 120% profit. I’ve been doing something similar with Amazon for almost 2 years and have had great results to date. I also did part of my DocuSign buy this way in early January. Since then, the stock is up 27% and my trade is ahead over 50%. Clearly if DocuSign (or Amazon or Zoom) stock runs I won’t make the same money as a straight stock purchase would yield given that I’m capped out on those DocuSign shares at slightly under 100% profit, but the trade also provides substantial downside protection.
Conclusion: Investing in Newly Minted IPOs of High Growth Companies with Solid Contribution Margins Can be Done in a “Value Oriented” Way
When deciding whether to invest in a company that IPOs, first consider the business model:
- Are they growing at a high rate of at least 30%?
- Experiencing increasing contribution margins already at 20% or more?
- Is there visibility to profitability without a landscape change?
Next, try to get the stock on the IPO if possible. If you can’t, is there a way of pseudo buying it at a lower price? The transaction I constructed may be to complex for you to try and carries the additional risk that you might wind up owning twice the number of shares. If you decide to do it make sure you are comfortable with the potential future cash outlay.