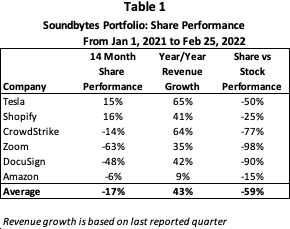
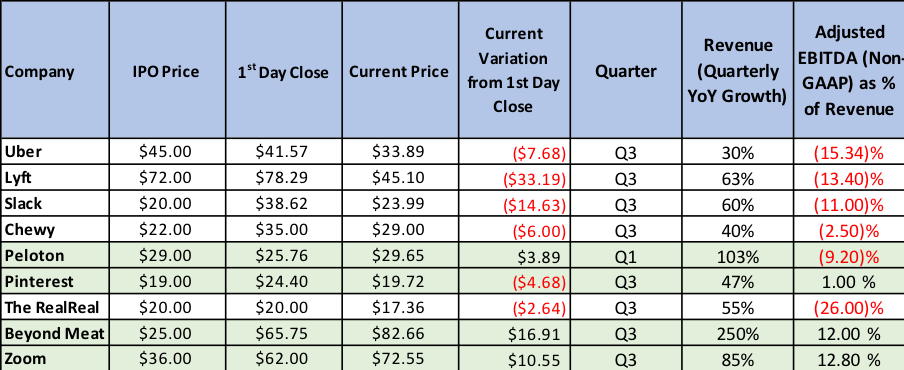
Last year was a very strong one for our top ten picks where all 10 proved correct, and our six recommended stocks were up an average of 96% with 3 of the 6 appreciating over 100%. While there is some risk in continuing to recommend them after such a strong surge last year, we believe they will perform well this year and already said (in the previous post) that each would be on the new list. The price per share we’ll use is as of December 31, 2023, for each (including Tesla which is down about 25% YTD). We are going to add one new stock to the group, Nvidia, which is a strong play on the push to AI as its chips are well ahead of others for that space.
The first 6 declined substantially in 2022 despite solid performance as they were victims of interest rates surging. The Fed has indicated that rates will likely decline in each of the next few years which should, in turn, help our “long-duration” stocks appreciate. The risk to this assumption is if inflation reverses its downward trend and surges once again. That could mean the Fed not only reverses its projection of declining rates but might increase rates once again. This would be quite negative for our stocks as there is a built-in assumption in the market that this will not occur.

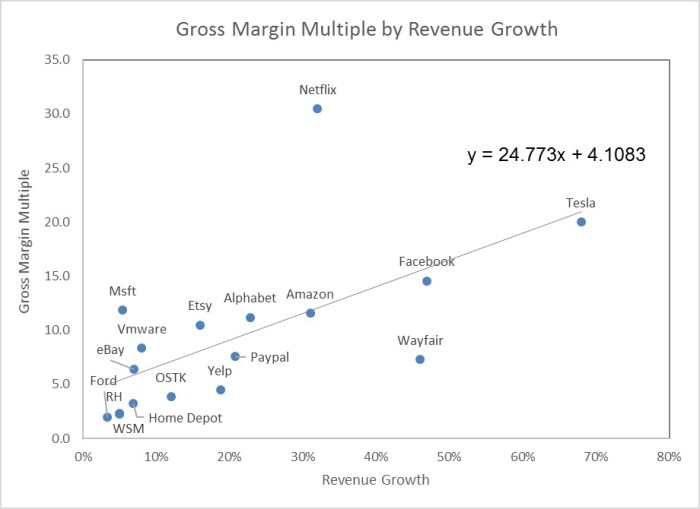
Even with the 96% average gain in 2023, in the past 2 years the average of the 6 (we’ll talk about Nvidia separately) is still down 18.6% despite average revenue expanding by 86% in the same period. What this means is the price/share to revenue has declined by 56% in the past 2 years. If we looked at this over 3 years the decline would be even steeper. So, even if one believes that these stocks were at an inflated price at the end of 2021, they do not appear to be inflated now. Given that they are all growth companies (with analyst estimates showing 5 of these 6 growing 20% or more in 2024 and the 6th, Amazon, growing over 11%) it appears to us there is still strong upside barring extraneous events that cause difficult market conditions.
Of course, there is another issue for bears to jump on – the potential for a recession. This could undermine company performance. It appears we are headed for a “soft landing” but that still is not a given, especially if rates don’t start coming down at some point in 2024.
I’ve often pointed out that I am not a great forecaster of economics or of the market as a whole so the above discussion may not mean inflation moderates further, or that Fed Rates decline, etc. Given the compression in revenue multiples across the board in tech stocks over the past three years (the three year decline was even greater than shown in our above two year table), the opportunity for investing still appears timely to me despite last year’s appreciation in the stocks.
2023 Stock Recommendations (Note: base prices are as of December 31, 2023)
1. Tesla will continue to outperform the market (it closed at $248.48/share)
While Tesla did appreciate over 100% in 2023, its stock still was nearly 30% lower than on December 31, 2021. This occurred even though revenue was up almost 70% in the same two-year period. And the stock is down over 25% YTD in 2024. While the company reached its target of over 1.8 million vehicles sold in 2023, it came at a cost of much lower gross margins leading to a very low growth rate for revenue in Q4 and disappointing earnings.
This plus several other issues have weighed on the stock:
- The Cybertruck, which has a massive backlog, is expensive to manufacture and could have very low gross margins until it ramps up to volume which is not expected until late this year. In 2025 it should add a more substantial number of units to Tesla sales.
- Elon keeps causing concern amongst investors with his behavior.
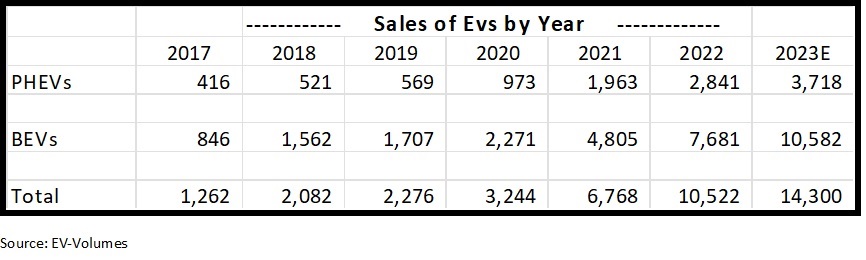
- The growth in sales of BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles which does not include Hybrids) seems to be slowing. We always expect high growth rates to decline over time but still believe sales of BEVs will grow over 20% per year for some time. See our blog post for a full analysis of why we expect BEV sales to grow at a high rate for the next 5 years.
- The strategy of lowering prices to drive share gain is working in terms of market share gains but has had a negative impact on revenue growth and profitability.
- Competition is getting stronger.
While we agree that the Cybertruck will likely take much of 2024 to ramp up production it’s important to realize that sales of this vehicle are incremental for growth so selling 90,000 units would add 5% to Tesla’s 2024 unit growth rate (and more to its revenue growth rate), 180,000 would add 10%. We’re guessing shipments will likely be between the two with more than half in Q4. The vehicle is so unique that it should also act as a draw for people to visit Tesla showrooms which will help sales of other models.
If Elon is a bit distracted that should not impact Tesla as its product road map is pretty well set for the next 3-5 years. If his comments cause a subset of people to decide not to buy a Tesla this may be offset by others liking them and considering the vehicle.
High growth rates almost always decline over time as a product scales. The growth in sales of BEVs cannot stay at the level it’s been at so it shouldn’t be a surprise that it is slowing. In 2022 BEV unit growth was about 60%, down from over 100% the year before. In 2023 it appears to be about 37%, still a very attractive rate. Because of high interest rates 2024 auto sales growth will moderate across all vehicle categories but we expect it to reaccelerate as rates decline.
The competition from Chinese manufacturers is getting stronger. But competition appears to be weakening from everyone else. In November General Motors announced a lowering of its sales and production goals. This month Ford announced a large reduction in investment in Electronic vehicles. In September Volkswagen cancelled its plans for a new factory for building BEVs. To us this means Tesla and one or two Chinese manufacturers are out executing traditional auto companies and gaining share. As more customers convert to BEVs we believe Tesla will continue to gain share of the overall market.
Analysts are predicting that Tesla will grow revenue by 15% -20% in 2024. We believe it could be higher given the introduction of the Cybertruck, expansion of sales of the Semi, and unit growth that we expect to be 25% or more. Revenue growth will be slowed by lower pricing vs the prior year in the first 2 quarters but helped by the ramp of the Cybertruck in the second half of the year. By Q3 Cybertruck sales will be more meaningful and the ASPs of other Tesla models vs Q3 2023 will be better. All in all, we expect Tesla to return to over 25% revenue growth by Q4 and potentially grow over 20% for the year as a whole. We believe this not only means that its stock will make up the ground it has lost YTD but could show solid appreciation over the close on December 31, 2023.
2. Shopify will outperform the market (it closed at $77.88 per share)
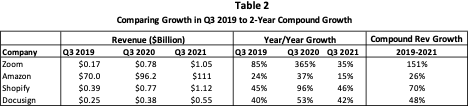
In our post of Top Ten predictions last year, we pointed out that the pandemic had created a major warping of Shop revenue growth. Instead of the normal decline for high growth companies from its 47% level in 2019 it jumped to 86% growth in 2020 and still was above “normal” at 57% in 2021. Once physical retail normalized in 2022, Shopify growth plunged against the elevated comps declining to a nadir of 16% in Q2, 2022. When we included Shop in our Top Ten for 2023, we pointed out that we expected its revenue growth to return to 20% or more throughout 2023. This indeed did occur, and Shopify revenue growth was about 25% for the year. We expect the 20% – 30% growth rate to continue in 2024 as:
- Net revenue retention for the company continues to be over 100% due to Shopify successfully expanding the services it provides to its eCommerce business customers. Additionally, because successful eCommerce companies are growing, Shopify also grows its portion of the customer revenue it shares.
- Shopify has emerged as the number one alternative to Amazon and larger companies are now being added to its customer base.
We believe Shopify remains an undervalued stock as its price to revenue is still 63% lower than at the end of 2021. Additionally, the company is now at the point of leverage where earnings should grow faster than revenue.
3. CrowdStrike will outperform the market (it closed at $255.17 per share)
CrowdStrike (CRWD) has now rebranded itself as the “AI Native Security Platform” given its leadership in using AI to prevent breaches. The company continues to gain a substantial share of the data security market. Given its leadership position in the newest technology coupled with what is still just over 3% of its TAM, CRWD remains poised for continued high growth. This coupled with over 120% net revenue retention for 20 straight quarters makes CrowdStrike a likely long-term grower at over 30% per year. High revenue retention is primarily driven by expanded module purchases where 63% of subscription customers now pay for 5 or more modules.
The recent threats by Russia to create a Cyber attack on the U.S. could be an additional boost to the entire security industry. CrowdStrike stands to be a disproportionate beneficiary as it has the most advanced technology for defending companies against such attacks.
4. Amazon will outperform the market (it closed at $151.75 per share)
As we forecast, Amazon improved revenue growth in each quarter of 2023 from its low point of 8.6% in Q4 2022. In Q3 2023 growth was back to 12.6%. Additionally, the company increased its focus on profitability with Q3 profits up well over 200% versus the prior year’s weak numbers. This coupled with the improved environment for tech stocks helped drive Amazon’s share price to $151.75 at year end, up 81% from the close on December 31, 2022. We expect revenue growth to exceed 12% in 2024.
While continuing double digit revenue growth will help, a second potential driver is that new CEO Jassy seems to have decided to increase the focus on earnings growth. This is available to Amazon if it chooses to do so. If he continues that trend, it could be a catalyst to share appreciation. For example, Prime remains a distinct bargain as it not only includes free shipping but also a number of other benefits such as video streaming of movies and TV shows, some free eBooks, discounts at Whole Foods and more. Given that Prime has over 220 million members, a $20/year increase for the subscription or additional monetization of content in that amount per user (which equates to less than one extra movie or TV series purchased every 4 months) would add over $4.4 billion to revenue once it fully rolls out. Such an increase is worth about $8 per share of earnings. Additionally, the company has meaningful AI technology that could drive additional revenue. Amazon has also been trimming costs (as a percentage of revenue). Given this combination, we expect earnings to grow faster than revenue in 2024.
5. Data Dog will outperform the market (it closed at $121.65 per share)
Like many other high growth subscription-based software companies, Datadog experienced another solid year in 2023 with Q3 revenue growth at 26.7%. Also, like CrowdStrike, Datadog has a very high gross margin (GM) and is now at the point where it has started to leverage its GM driving up earnings (+96%) at a much faster rate than revenue. While the stock was up 66% in 2023, it is still down 32% over 2 years despite Q3 2023 revenue being 195% higher than Q3 2021.
6. The Trade desk (TTD) will outperform the market (it closed at $71.80 per share)
Every 4 years we point out that political spending in a Presidential election year adds an additional layer of revenue to the advertising space helping it have an above normal year of growth. In 2024 there are 3 additional factors that should help drive accelerated growth (discussed in prediction 9). CTV (Connected TV) has been gaining share of the space and The Trade Desk remains a leader in CTV. Analysts are forecasting 20% revenue growth for the company in 2024. We believe an increased market size coupled with share gains should help TTD grow revenue at an even greater rate. We believe such a result will lead to another year of solid stock performance.
7. Nvidia will outperform the market (it closed at 495.22 per share on December 31, 2023)
Nvidia is one of the strongest ways to invest in the coming AI evolution. Its generative AI-optimized GPUs have a technology lead on its competition and are needed by companies moving to AI. The demand for such a product currently exceeds supply, giving the company several quarters of backlog. Because of the shortage supply coupled with a superior product Nvidia has significant pricing power.
In Q3 the company’s revenue grew over 200%. Because its gross margin was up to 75% the combination drove earnings of $4.02 for the quarter up nearly 7X from the prior year’s $0.58. Based on current earnings forecasts the stock is not expensive, trading at about 30X analyst earnings forecast for fiscal 2025 (year ending in January 2025).
Make no mistake, this will be a volatile stock given its startling growth. The question of whether current pricing can be maintained as stronger competition emerges could be an overhang. AMD launched a competitive product in December. It expects to ship as much as 400,000 GPUs in 2024. But, to put it in perspective relative to demand, Nvidia is forecasting shipping 1.5-2.0 million GPUs this year up from about 550,000 in 2023. This would mean AMD is projecting unit sales of about 25% of Nvidia units in 2024. It seems unlikely that AMD will try to force down pricing in 2024. Also, in general, the cost of manufacturing chips declines as a product matures so even if pricing declines 20%, gross margins could remain close to where they currently are. Intel is also working on becoming a leader in AI. It has several products and numerous customers but appears to be trailing Nvidia (and AMD) in technology.
A second potential issue for Nvidia is sales to China which comprised over 20% of its sales in Q3. The US government has restrictions on selling the most advanced technology to Chinese companies and Nvidia believes it has complied. The company also stated that it expects the percent of sales to China to decline in Q4.
For now, we believe Nvidia will continue its momentum throughout 2024 and beyond. Given that demand is growing rapidly (there are forecasts that 80% of all PC sales will be AI enabled in 4-5 years) pricing pressure that causes significant GM decline appears unlikely to emerge in the next 2-3 years. As we saw in the PC space (where Intel controlled things), as pricing on older chips declined, users tended to buy newer technology meaning that instead of paying less for the older product they paid what they had before for a more powerful product. It appears that the AI space is still young enough to replicate this trend.
8. Other “AI” Companies will emerge as strong performers.
Like the PC revolution in the 90s and the web from 2000 onward, AI appears to be a new generation for products that will lead to existing companies re-inventing themselves and new ones emerging. Each of the prior decades-long trends spawned numerous successes. It appears that AI will be the next generational change in technology. It will dominate thoughts on Wall Street for the next decade or more with numerous winners emerging. While it’s hard for us to tell who else besides Nvidia, CrowdStrike and Tesla will distinguish itself as an AI leader and generate high revenue growth rates there are a number of candidates that are at the table.
In the chip world, AMD seems a strong candidate. Intel is trying to transform itself to another candidate but it has a large share of existing sales, so it needs to become a leader to generate enough new revenue to offset its loss of more traditional sales. IBM is inserting AI chips into its products which could mean a resurgence of demand for servers at higher pricing and margins. The same could be said for PC manufacturers.
While chips and hardware are the first stage of revenue generation from AI, hosting services from Microsoft, Amazon and others could be the next step in rolling out AI. They can potentially increase pricing and also grow their services. Social networks will also benefit but I’m not sure how someone like Meta can drive enough growth in monetization.
Security is already an important use of AI and CrowdStrike has utilized it to great effect. Others like SentenilOne are following in their footsteps. Gaming is another arena where AI will be important. And autos need to utilize it if autonomous self-driving cars are to become dominant. Tesla is at the forefront in creating such success with Waymo another very important player.
One of the most exciting arenas for AI is in robotics. Tesla is working on a robot that will heavily utilize AI to manage its movements, but a commercial product seems years away.
9. Furniture and Home accessories will stage a comeback in 2024, returning to growth.
Not surprisingly, home sales diminish when higher interest rates on mortgages increase the cost of ownership. And when this happens very quickly sellers are slow to reduce prices to reflect the inability of buyers to pay the same price as when rates were lower. The result last year was that US home sales hit a 30-year low. Additionally, homeowners taking out loans to remodel also stalled due to the higher rates. Sales of furniture and related accessories are highly correlated to home purchases and home remodels and were down 5-10% in 2023 vs 2022. Now that some time has passed where owners had difficulty selling their homes many are lowering prices making the cost of ownership more affordable. Also, The Fed is expected to stabilize and then reduce rates this year. This combination should lead to more home purchases and home remodels. Given the “easy comps” and built-up demand we expect furniture and related accessory sales to return to double digit growth during 2024 after a year of declining revenue.
10. Advertising revenue will have a comeback in 2024.
Advertising revenue was hurt last year by the economy as well as several short-term issues like the decline in furniture sales discussed in prediction 9. Many advertisers cut back spending due to issues with the economy. Stable interest rates should lead to increased spending by advertisers of goods and services.
Advertising also took a major hit from strikes in the auto industry and Hollywood. In each case this led to a loss of ad revenue. Without many new movies and shows media advertising was cut dramatically (no pun meant). And of course, GM, Stellantis (formally Fiat/Chrysler) and Ford cut their spending during the union strike.
Political spending on advertising mostly occurs in even years when the bulk of elections take place. Every fourth year this is boosted by the presidential primaries and election. Group M estimates that advertising spending (excluding about $1B spent on direct mail) will be about $16 billion dollars this year, up over 31% from the 2020 election year. While the bulk of the dollars will be spent on TV, online platforms like Facebook and Google will benefit as well. This also is likely to be the first presidential election where AI tools are used to improve targeting of potential campaign contributors.